Lithium metal Two weeks ago, we reported on Karma Automotive, Inc. and Factorial, Inc. announcing the launch of the first solid-state battery production program in the US for passenger vehicles, batteries that will use lithium metal. Going over a white paper from Factorial line by line failed to adequately address how the volatile metal is …
Category: Electric and Electrified Vehicles
Discussions of hybrid, plug-in hybrid and battery powered vehicles and technology.
Permanent link to this article: https://dashboardsymbols.com/2026/02/hyundai-snags-two-of-six-edmunds-best-of-2026/
Permanent link to this article: https://dashboardsymbols.com/2026/02/factorial-silent-on-lithium-metal-use-in-ev-battery/
A warmer week pushes range boost
Range boost A single week with high temperatures at or near 40 F has left its mark on the Kia Niro electric vehicle (EV) with 20 mile range boost. This week’s charge has us back at 230 miles, extrapolated from the 90% charge result shown below right. This is the same number seen for most …
Permanent link to this article: https://dashboardsymbols.com/2026/02/a-warmer-week-pushes-range-boost/
Karma, Factorial to build first solid-state battery powered EV
Solid-state battery Karma Automotive, Inc. and Factorial, Inc. have announced the launch of the first solid-state battery production program in the United States for passenger vehicles. The pair will integrate Factorial’s FEST® battery technology into Karma’s next-generation vehicle platform, beginning with the all-electric Karma Kaveya super-coupe scheduled to arrive on American roads in late 2027. …
Permanent link to this article: https://dashboardsymbols.com/2026/02/karma-factorial-to-build-first-solid-state-battery-powered-ev/
Continued cold fails to harm Niro EV range
Niro EV range The east coast of the U.S. continues to suffer from an extended cold snap the likes of which has not been seen in decades. Despite this, the Kia Niro EV range has held. Sure, it is less than what it experienced a year ago, but temperatures since mid-January and early have exceeded …
Permanent link to this article: https://dashboardsymbols.com/2026/02/continued-cold-fails-to-harm-niro-ev-range/
Marquee models sacrificed as Tesla EV sales plummet
Tesla EV sales In a clear sign of trouble at the company, CEO Elon Musk says that production of the Model X and Model S will be discontinued “next quarter” as Tesla EV sales continue to skid. According to the Guardian, in the latest investor call, Musk said “It’s time to basically bring the Model …
Permanent link to this article: https://dashboardsymbols.com/2026/01/marquee-models-sacrificed-as-tesla-ev-sales-plummet/
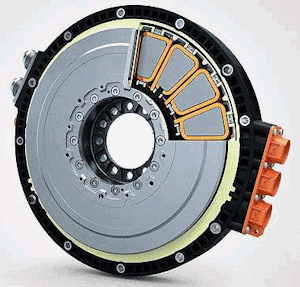
New YASA electric motor promises more power from less mass
YASA electric motor It turns out that the YASA axial flux electric motor has been in development for about 20 years, but a video just found its way into my algorithm. Likely as a result of the attention we gave to the solid-state battery and Donut motor from Verge Motorcycles in the last few weeks. …
Permanent link to this article: https://dashboardsymbols.com/2026/01/new-yasa-electric-motor-promises-more-power-from-less-mass/



Hyundai snags two of six Edmunds best of 2026
Edmunds best The recently released Edmunds best of 2026 list includes two entries from Hyundai. In fact, of the over 500 cars and trucks evaluated buy the group, the Hyundai Palisade Hybrid came out on top as the Best of the Best for 2026. As the best SUV for the year, Edmunds gave the three …
Continue reading